3 keys to efficient water consumption in data centres

Data centers have become the heart of global technological infrastructure. These large facilities are crucial for the functioning of the Internet, data storage, and support of critical applications. However, behind their uninterrupted operation lies a significant challenge: sustainability. Data center operations require vast amounts of energy and water, resulting in a considerable water and carbon footprint.
Through innovation and optimization, it is possible to move towards more sustainable and efficient operations. In this context, CIRCE - Technological Center positions itself as a strategic ally to face these challenges and lead the transition towards a greener future.
What is the water footprint?
The water footprint is a metric that reflects the total volume of water used, directly or indirectly, to produce a good or service. In data centers, this footprint mainly manifests through water usage for server cooling and energy generation, which keeps operations running. Given the growing demand for digital services, the need for water in these centers is increasing, making efficient and responsible management of this resource crucial.
Why is the water footprint so important in data centers?
The significance of the water footprint in data centers cannot be underestimated. Beyond its direct impact on local water resources, a high water footprint can increase operational costs and jeopardize the long-term sustainability of the facilities. Therefore, addressing this challenge is essential not only from an environmental perspective but also from an economic and operational standpoint.
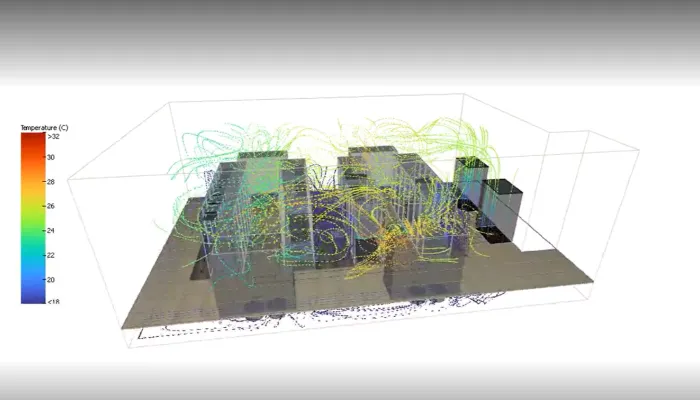
This is why we must not forget two important indicators when tackling this challenge: WUE (Water Usage Effectiveness) and PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness). Addressing them in combination allows data centers to minimize resource use while maximizing performance. There are various key technologies driving energy efficiency and sustainability in data centers, helping to reduce their environmental impact.
Beyond calculating the water footprint
Reducing the water footprint is an essential step toward the sustainability of data centers. It is not just about reducing water consumption but also about improving overall operational efficiency. Cooling systems, which are the main consumers of water in data centers, are also responsible for a significant portion of energy consumption. By optimizing these systems, a simultaneous reduction in water and energy usage can be achieved.
Moreover, water usage efficiency can enhance the resilience of data centers against potential water shortages and changes in environmental regulations. In this way, operators not only comply with regulations but also position themselves as leaders in environmental responsibility, a quality increasingly valued by investors and clients.

What are the most effective strategies to reduce the water footprint in data centers?
Reducing the water footprint in data centers requires a multidisciplinary approach, ranging from the implementation of new technologies to the optimization of existing processes.
The most effective strategies:
Advanced cooling technologies:
- Adiabatic cooling: uses the natural process of water evaporation to cool the air, allowing for a significant reduction in water usage compared to conventional cooling systems.
- Air cooling and non-aqueous liquid cooling: these systems minimize or even eliminate the need for water, using air or special fluids instead to allow efficient heat dissipation.
Water reuse and recovery:
- Water recovery systems: by capturing and reusing water used in cooling processes, data centers can reduce their reliance on fresh water sources.
- Reuse of wastewater: treated and recycled water can be reused in the cooling process, decreasing the demand for new water and reducing the overall water footprint.
- Industrial symbiosis: collaboration between companies to reuse water, minimize contaminated water, optimize resource use, and develop sustainable technologies.
Design and operation optimization:
- Water consumption monitoring and management: implementing Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and advanced management systems allows real-time monitoring of water consumption, identifying opportunities to improve efficiency and detect leaks or inefficiencies.
- Efficient architectural design: proper planning of airflow and server layout can reduce the need for additional cooling, optimizing both energy and water usage.
Reducing the water footprint in data centers is not just a matter of environmental sustainability but also of operational efficiency and long-term viability. Therefore, CIRCE – Technological Center helps data centers tackle water footprint reduction as part of their energy and resource efficiency strategy.

Latest news